Learning with LLMs
The Two Paths
LLMs like ChatGPT, Claude, and Gemini can generate quick data analysis solutions—but relying on them too much can impede your learning.
When you hit a problem, your brain’s first instinct is often: “I’ll just prompt the AI to write this for me.” It’s the path of least resistance—fast, easy, done. But here’s the thing: you’re here to learn, not just to get answers.
This is where you need to engage your slower, more deliberate thinking. Pause and recognise the choice in front of you. There are two paths you can take, and they lead to very different destinations.
Path A is the trap—it feels productive but leaves you with shallow understanding and eroding skills. Path B is the goal—it takes more effort, but builds genuine mastery and self-reliance.
The diagram below shows how each path unfolds. Every time you reach for AI, ask yourself: which path am I about to take?
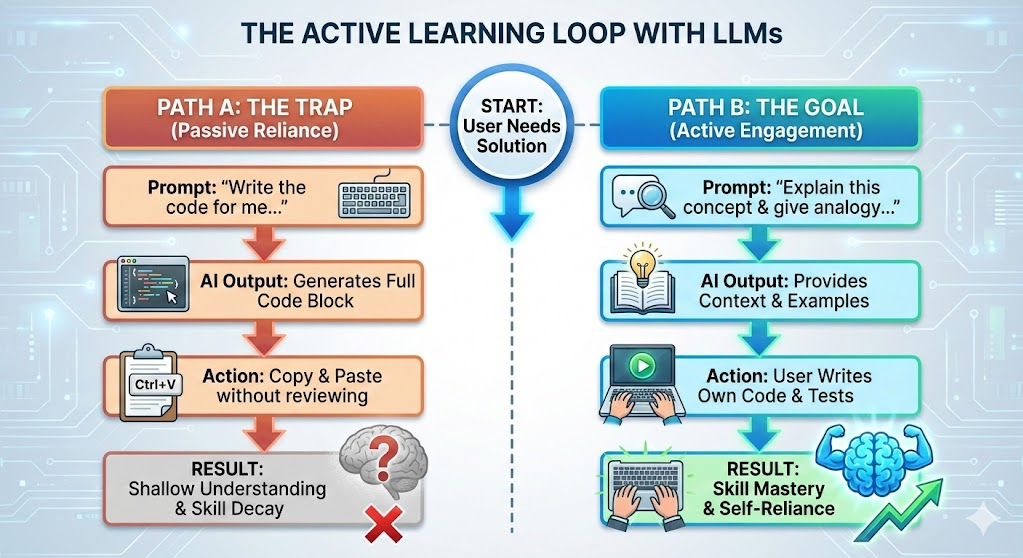
The good news? LLMs can be outstanding tutors and mentors when used the right way. This page will help you follow Path B—using AI to build understanding rather than bypass it. This is what Principle 3 is all about.
Try these prompts in your AI tool of choice and consider how they differ from your current prompting methods.
Using LLMs to Learn Effectively
🧑🏫 As a 24/7 Tutor & Mentor
You can use an LLM as a personalized data analysis tutor, one that explains concepts at your level, gives examples, and answers follow-up questions.
Example Prompt:
Act as a Pandas tutor for a beginner. Explain how groupby() works
with aggregation functions, and give clear examples.🧠 The Socratic Method
Instead of asking for the answer, ask the AI to guide you to the answer. This prevents you from passively reading and forces you to think.
Example Prompt:
I am learning about Data Analysis (specifically Pandas and Data Cleaning).
Don't give me the answers or write the code for me yet.
Instead, ask me a conceptual question to test my understanding of how to handle missing data or filter rows.
If I get it wrong, give me a hint regarding the logic (not just the syntax) and ask again. 🧩 To Explain & Simplify Concepts
LLMs are great at breaking down complex data analysis topics into simple, digestible explanations.
Example Prompts:
Explain the difference between merge() and join() in Pandas.
When should I use each?What does pivot_table() do in Pandas? Give a beginner-friendly
explanation with a practical example.🕵️♀️ Visualising Code Execution (Dry Runs)
In data analysis, the hardest part isn’t usually the loop logic—it’s tracking how the shape and content of your dataframe changes after each operation (filtering, merging, grouping). You can ask an AI to perform a “Dry Run” or create a Trace Table. This shows you exactly how your dataset evolves step-by-step.
Example Prompt:
Here is a block of Pandas/SQL code I wrote to clean my data.
Please perform a "Data Trace" of this code.
Create a step-by-step summary showing:
1. The dimensions of the data (rows x columns) after each line runs.
2. A visual sample of what the data looks like at that specific step.
3. A specific explanation of which rows or columns were dropped or modified and why. 💡 For Brainstorming & Problem-Solving
Stuck on how to approach a data analysis task? Use AI to explore different approaches and plan your workflow.
Example Prompt:
I have a dataset with missing values in multiple columns.
What are different strategies for handling this, and when
should I use each approach?🔍 As a Code Reviewer & Optimizer
LLMs are excellent at reviewing your code, helping you improve readability, efficiency, or structure.
Example Prompt:
Here's my Pandas code that filters and groups rainfall data.
Can you suggest improvements or a more efficient way using
method chaining?Asking for feedback, instead of code generation, encourages active learning—exactly what Principle 3 is about.
Concepts to Explore with AI
Try using AI to deepen your understanding of essential data analysis topics:
- Pandas data structures:
DataFrame,Series,Index - Data loading:
read_csv(),read_excel(),read_json() - Boolean indexing vs
.loc[]vs.iloc[] - Grouping and aggregation:
groupby(),agg(),transform() - Reshaping data:
pivot(),pivot_table(),melt() - Merging and joining:
merge(),join(),concat() - Handling missing data:
fillna(),dropna(),interpolate() - Method chaining for cleaner code
- Matplotlib chart types: line plots, bar charts, scatter plots, histograms
- Customizing visualizations: colors, labels, legends, subplots
AI tools aren’t just for answers anymore—they’re becoming interactive tutors.
ChatGPT’s Study Mode turns the chatbot into a thoughtful tutor that guides learning step-by-step using Socratic questioning and personalized feedback. It’s available to users across Free, Plus, Pro, and Team plans.
Gemini’s Guided Learning taps into the LearnLM model—trained with learning science principles—to lead you through topics thoughtfully. Expect multimedia support (like images, diagrams, videos), quizzes, and adaptive explanations.
These features turn AI into a collaborative learning companion—encouraging curiosity, deeper comprehension, and active engagement rather than just delivering quick answers.